When your sensitive information
starts appearing in your
competitor’s hands, you might think
it’s an external
breach. But sometimes, the
culprit is much closer someone you
trust.
Malicious Insiders Might
Be to Blame!
Yes!
In this
blog, we’ll uncover who they are,
why they act, and how you can
protect your company from becoming a
victim of internal threats.
What is a Malicious Insider?
A malicious insider is an employee or
trusted individual within an
organization who intentionally uses
their access to systems, data, or
resources to harm the organization,
typically by stealing, damaging, or
leaking sensitive
information.
Unlike hackers
from outside the company, malicious
insiders already know how things
work and have direct access to the
company’s systems. This makes it
much harder to catch them in the
act. Because they understand the
company’s inner workings, their
actions can be far more damaging.
What Motivates Malicious Insiders?
Malicious insiders don’t act without
a reason. While their actions can
harm an organization, understanding
their motives is the key to
preventing these risks.
Let’s
look at the main reasons behind this
behavior.
1. Financial Gain
A major reason malicious insiders harm a company is for financial gain. Some people inside a company are driven by the lure of money. They might steal the company’s confidential information, such as customer data, product designs, etc., and sell them to competitors for personal profit. Some may sneak money out of the company through tricks. Some may change things in the system to make extra money or cover up what they’ve done. Sometimes, employees might take bribes or rewards to share company secrets with outsiders.
2. Revenge or Grudge
Employees may turn against the organization because they feel mistreated or have some personal issues with their co-workers.
Yes! It may happen!
For instance, if employees feel they’ve not been treated fairly, like not getting the promotion they deserved or being fired without a good reason, they might get upset and want to get back at the company. At that moment, they could hurt the company by messing with its systems, such as deleting important files or sharing private information. Sometimes, any problems with colleagues or bosses can mess up things such as spreading rumors, unnecessary gossip, causing trouble, etc., to hurt the company.
2. Social or Peer Influence
Employees make bad choices because of pressure from people around them. They might be influenced by friends, family, or coworkers who push them to steal or cause problems. At times they may develop allegiance to a certain group at the workplace and end up harming the company to favor that group. They might believe they are helping their friends or looking out for themselves, even if it ends up hurting the company. This kind of pressure can lead them to make decisions that they wouldn’t normally make.
Malicious Insider Threat Examples

1. Data Theft
Data theft is one of the most troubling insider threats, where trusted employees misuse their access to sensitive information for personal gain. For instance, if a financial service worker secretly exposes the clients’ details such as social security numbers, account details, etc.
In just a few minutes, an employee can sell this data to outside groups, putting the privacy of many clients at risk. Imagine a healthcare worker with proper access to patient records who secretly copies this information and makes money by selling it on hidden websites. In each case, an employee is turning their company’s trust into a dangerous vulnerability, impacting client trust and costing the business dearly.
2. Corporate Espionage
Corporate espionage is the secret side of competition, where insiders act as spies, sharing valuable company information with rivals to give them an advantage. This isn’t random—it’s often carefully planned.
For instance, an employee may leak project details or business strategies to a competitor to receive a better job offer. Although such employees may have access only for a short time, they might misuse their opportunity by copying files or releasing confidential information. These kinds of betrayals don’t just harm a company today—they can threaten its future by turning its strengths into weak points and putting its success in danger.
3. Sabotage
Sabotage is usually carried out by IT people who have strong technical skills, such as system administrators or software engineers, and are usually driven by feelings of unfair treatment or revenge. They use their strong skills to intentionally harm the organization, which makes them hard to find.
For instance, a software engineer might write the wrong code that deletes all important logs, or might change passwords, and prevent other employees from doing their work.
How to Prevent a Malicious Insider Threat?
Do you think preventing malicious insiders is a tough task? Think again! With a few simple strategies, you can easily spot and stop insider threats before they cause any harm. Check out the steps below to protect your company and keep your data safe!
To prevent malicious insider threats, the organization should only allow authorized personnel to access sensitive information and keep an eye on what employees do. Limit access so employees can only see what’s necessary for their work. Improve security awareness among employees and develop procedures regarding the utilization of company information. Finally, the software that recognizes such activity and blocks data transfer should be used so that the security team will know about it and correct the situation.
Real-World Examples of Malicious Insider Incidents
These real-life examples will show you how serious insider threats are, and the huge damage they can cause. They reveal how trusted people can misuse their access, causing harm that’s not just about losing money—it can destroy a company’s trust and reputation.
- In March 2020, a man named Christopher Dobbins was fired from a medical supply packaging company. After getting his last paycheck, he went back into the company’s computer system without permission. He gave himself high-level access and then changed and deleted about 120,000 important records. This caused big delays in getting medical supplies to hospitals when they were needed the most.
- In June 2022, a Taco Bell worker was caught using customers’ credit card information for personal purchases. The police got involved when a customer reported an unauthorized charge at a local Pizza Hut. During the investigation, police found out about 36-year-old Laquawanda Hawkins, who was working at Taco Bell’s Drive through. Security cameras caught her taking pictures of customers’ cards and then using the details to shop in stores and online.
- In October 2020, Amazon informed customers that an employee had shared their email addresses with an unauthorized third party. Amazon initially claimed that a single employee had shared customer email addresses with an unauthorized third party, leading to their termination. This wasn’t the first time Amazon faced such a breach, as they had sent similar notifications about customer data leaks in January 2020 and November 2018.
- Anthony Levandowski worked as an engineer on Google’s self-driving car project. Before leaving to work at Uber, he stole over 14,000 important files. He copied these files to another disk and deleted the laptop to try and conceal the theft. This caused a legal dispute, and Uber eventually paid $245 million to settle the case.
- In 2018, police in Ukraine reported that a man tried to sell 100GB of customer data to his former employer’s competitors for just $4,000. In 2018, a man used his knowledge of his former company’s weak security to steal 100GB of customer data. He tried to sell it to his ex-employer’s competitors for $4,000.
How Does Time Champ Help Prevent Malicious Insiders?
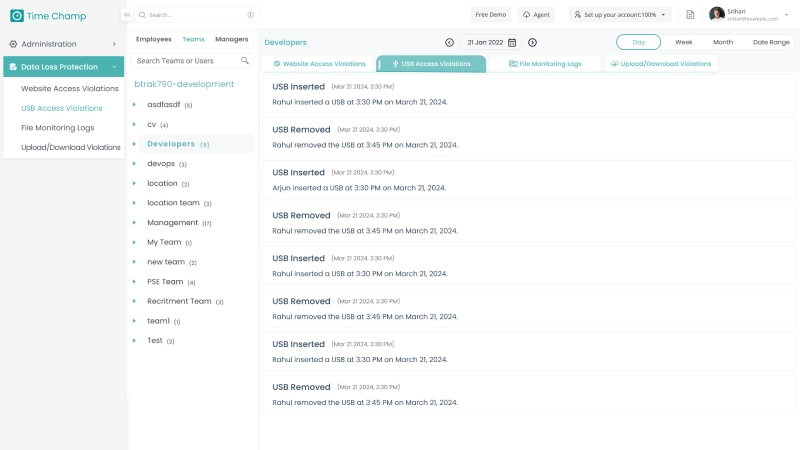
Time Champ helps protect your organization from insider threats with its strong Data Loss Prevention (DLP) system. With its website blocking function, it helps employees stay focused by blocking distracting or unsafe websites. These websites are configured as safe or unsafe by the employer to ensure secure browsing. This makes sure that they stay on task and prevents unnecessary security risks, keeping your business safe and productive. In addition, Time Champ’s USB Device Control will enable you to suspend or monitor the functionality of USB devices to ensure data leakage is prevented. The File System Change Monitoring feature provides real-time alerts, so you’ll always know if someone tries to tamper with important files. Time Champ’s Attachment Control feature prevents any type of file that is likely to leak sensitive details from being uploaded or downloaded by employees.
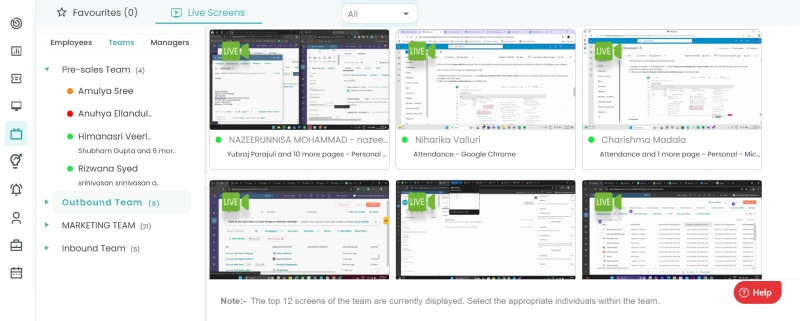
Along with it, Time Champ’s employee monitoring helps you identify malicious insiders with ease. You can capture employees’ screenshots at customizable intervals, record their live screens, and even view their screens in real-time, providing valuable documentation for investigation. Its silent mode works discreetly in the background to detect and prevent harmful actions, ensuring sensitive data is protected and minimizing insider risks.
By using these features together, Time Champ helps protect your organization’s data and prevent internal threats, all while keeping everything running smoothly and efficiently.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, malicious insider threats causes huge damage to organization in many ways. However, these threats result from different reasons, but the effects are always terrible. Businesses need to take proactive steps for their protection: restricting access to sensitive information, monitoring employee activity, and encouraging a security-first culture. The right tools and actions help businesses reduce insider threats and keep their data safe. By focusing on security and always finding better ways to manage risks, companies can protect their future and keep their customers’ trust.
Stop Insider Threats with Time Champ’s DLP Solution!
Empower your organization to prevent data breaches with our advanced security features!
Signup for FreeBook DemoFrequently Asked Questions
A malicious insider is an employee who exploits their access to intentionally harm the company, often fueled by personal motives like greed, revenge, or resentment. Unlike external hackers, insiders have an inside track—they know the company’s systems inside out, making their actions not only harder to detect but also far more dangerous.
Yes, former employees can still be a threat. To avoid this, companies should revert the access and have an audit system to avoid any risks.
Malicious insiders are hard to spot because they have trusted access and know the company’s systems, allowing them to exploit weaknesses without triggering alarms.
The consequences can include jail, fines, and lawsuits for stealing information. To protect the company’s reputation, it’s best to take legal action to get back anything that was stolen.







