Have you ever thought about the risks that could come from within your organization? Sometimes, the biggest threats aren’t from the outside but from trusted individuals inside. Managing these risks can seem challenging, but it’s not impossible. Insider threat mitigation is about understanding these risks and taking steps to handle them effectively. In this article, we’ll explore ways to prevent insider threats and protect your organization.
What is Insider Threat Mitigation?
Insider threat mitigation is the act of finding out, controlling, and minimizing risks posed by insiders who have intentionally or accidentally linked with company contents, information, or operations negatively. This involves implementing strategies, policies, and monitoring systems to detect and prevent potential insider risks, helping protect sensitive information and maintain organizational security.
Best Practices for Insider Threat Mitigation
Based on Ponemon Institute research, insider threats are increasing with over 13 negligence-related cases on average across organizations and an upswing in credential theft. Such threats can take a lot of time to solve, so it is important to have robust preventive tools. Here are several best practices that may be put in place to reduce the chances of insider threats and bolster security.

1. Create a Comprehensive Insider Risk Program
You might think your chief information security officer (CISO), and security teams can handle all the insider threats, but they can’t see everything. Why? Because they don’t have the visibility into employee engagement or job satisfaction the HR and operations teams do. So, why not bring everyone together?
A comprehensive insider risk program isn’t just a checklist, it’s a collaboration. Your program should include cross-departmental teams made up of security, HR, IT, operations, and leadership. This way you can spot early the indicators of insider threat, whether it’s a disgruntled employee or someone who handles sensitive data too casually.
By including the right stakeholders, your program should aim to:
-
Pinpoint critical data and areas vulnerable to insider threats.
-
Identify high-risk individuals, like those with access to confidential information or those showing signs of dissatisfaction.
-
Set up a risk management process, including tools to monitor employee behavior and flag potential threats in real time.
Having an overall, company-wide risk program means you’re not just looking for threats to arise from outside the organization but are constantly considering and assessing insider vulnerabilities across departments.
2. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
It’s not enough to think you’ve addressed all your risks once. You need to keep testing and reassessing, especially as your company evolves. Regular risk assessments are vital for staying ahead of emerging insider threats. Without repeated evaluation, gaps in your systems, processes, or employee behavior might be discovered too late.
Here’s how to conduct an effective risk assessment:
-
Review the employee’s access rights to ensure they’re still necessary and appropriate.
-
Analyze patterns to ensure workplace efficiency and identify risks whether sensitive data is mismanaged or accessed improperly.
-
Analyze employee behavior and identify their work patterns. The patterns could be disgruntled employees or massive downloads of data.
Risk assessments should be performed quarterly, or whenever there are major company changes such as new systems, policies, or employees, to ensure new vulnerabilities aren’t overlooked.
3. Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
Data breaches don’t always come from outsiders; sometimes, the threat comes from those inside the company. A solid Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solution is your first line of defense. These tools monitor and block unauthorized data access, transfers, or sharing, preventing insiders from mishandling sensitive information.
Think of your DLP as the guardian of your sensitive data. With hybrid work becoming more common, you need data loss prevention tools that protect across various points of entry:
-
Endpoint DLP: Endpoint DLP tools manage data flow on devices like laptops, smartphones, and USB drives. They prevent the employee from moving company data to unauthorized locations or external devices. This protects the data when it leaves the company’s internal network.
-
Cloud DLP: Protecting your data in cloud services is crucial. Cloud DLP protects data shared through Google Drive, Microsoft 365, or Salesforce by preventing an unauthorized party from accessing it or distributing any company-sensitive information. This is very useful for a modern remote work environment where employees access information across multiple platforms.
-
Network DLP: Networl DLP will protect your data as it is transmitted through your network, including emails, web traffic, and file transfers. It can check for suspicious transfers or data sharing. It can prevent leaks that could hit your company via email or unapproved devices.
DLP tools aren’t just about prevention; they provide real-time alerts, so you can catch potential threats before they escalate into something more damaging.
4. Monitor and Manage Anomalous Employee Behavior
Most insider threats don’t come out of the blue; they start with abnormal behavior. Employees don’t just suddenly decide to steal data or sabotage systems. The warning signs appear gradually. By implementing behavioral monitoring tools, you can track and spot signs of unusual activity early.
Here’s how to keep an eye out for red flags:
-
Monitor system usage: Look for employees who access information that they do not typically require or need for their job. Are they going into prohibited parts of the network? Or are they downloading files on topics other than their job responsibility? These can be a hint that someone is accessing the wrong information or sending sensitive data.
-
Track unusual working hours: Is an employee logging sensitive data at odd hours of the night or during off-hours? Unusual login times could indicate attempts to cover up suspicious activities or engage in unauthorized access without drawing attention.
-
Watch for data anomalies: Are some employees downloading or transferring more data than usual? Such anomalous activity spikes especially when access to high-value data, could be a precursor to data theft or leaks. Watch for attempts to move large amounts of data to unapproved places, like personal drives or external networks.
Behavioral monitoring should be applied ethically, not to micromanage but truly to protect company assets from potential insider threats. The bottom line is the early spotting of risks, not invading anybody’s privacy.
5. Provide Ongoing Security Awareness Training
Employees need to know how to identify and report security threats, which include insider threats. Ongoing security awareness training has to keep your crew informed and prepared. Since security threats are constantly changing, your training should, too.
Here’s how to make the training effective:
-
Make it engaging: Use real-life scenarios. They will teach employees about phishing, social engineering, and safe data handling. For example, send a simulated phishing email. Then, check how your employees react. Finally, suggest ways to improve their vigilance. This kind of hands-on training can make security awareness relatable and memorable.
-
Update regularly: Train on new risks, like remote work vulnerabilities and new security protocols. As cyber threats evolve, we must keep training relevant. Topics like how to connect safely to company networks from personal devices, and the risks of unsecured Wi-Fi networks, are key.
-
Gamify it: Create quizzes or interactive lessons to make learning more engaging and memorable. A team challenge or a reward for high scores on security quizzes can be a great way to encourage employees to stay vigilant about security measures.
Your best defense against insider threats comes from having your team educated. Security awareness is not one-off training; it’s the ongoing process of keeping everyone engaged and alert.
6. Enforce Strict Authentication and Authorization Controls
You can’t afford to leave doors wide open. Authentication and authorization controls appear to be of great importance in reducing insider threats. Only those who need access to sensitive data or systems should be able to get in.
Here’s how to tighten up controls:
-
To protect the organization’s sensitive assets, ensure your employees use multi-factor authentication (MFA) while accessing special systems or data. MFA is the enhanced security measure where the user has to enter at least two or more credentials such as a password and a code received on a mobile phone. This makes user access even more secure especially when their password has been stolen by a third party.
-
Implement role-based access control so that all members of the team are allowed permissions only up to the requirements of their role. A finance member may need access to the financial records. However, they should not access the HR or IT systems. This limits the damage if an insider causes some unintended harm.
-
Regularly check your access levels to make sure the permissions are still appropriate for your job responsibilities. Periodic audits will help find outdated or unnecessary rights to access, especially considering changes in roles or a transfer of personnel in departments. Removing excess permissions is essential for maintaining security.
By implementing these controls, you are also minimizing the probability of an insider gaining or transmitting any valuable information within the organization without the permission to do so.
7. Establish a Reporting Program for Suspicious Activity
A reporting program is crucial for identifying potential insider threats early. Employees should feel comfortable reporting suspicious activities without fear of retaliation. Diverse reporting options are needed to protect the parties involved. There must be at least two reporting channels. They may include online forms for anonymous reports or a security person to whom cases can be reported.
Make sure your program includes:
-
Clear reporting procedures: Explain to employees the steps for reporting problems and the details they need to provide (who, what, when, and where).
-
Confidentiality: The results of such reports must be assured to remain anonymous so that employees can freely escalate any issue they come across.
-
Incentives: Provide incentives to those who report threats before they escalate.
The great thing about having a proper reporting program in place is that your team remains on high alert so insider threats can be caught before they do too much damage.
8. Develop Proactive Incident Response Plans
When an insider threat occurs, the damage can be swift and devastating. A proactive incident response plan means your team is ready to act. This reduces and prevents potential damage.
Your response plan should include:
-
Clear expectations and definitions of roles and responsibilities of each member of the team during the incident.
-
It must contain a descriptive process of identifying and isolating the threat so that further damage is controlled.
-
Communication protocols ensure real-time information of the key stakeholders while the problem is solved in the shortest time possible.
Test your plan with drills and simulations so everyone knows their role in the event of an incident. Proactive planning minimizes the chaos and damage from inside threats.
Benefits of Proactive Insider Threat Mitigation
Richard Clarke once said, “If you spend more on coffee than on IT security, you will be hacked. What’s more, you deserve to be hacked.” This stresses the importance of focusing on proactive security to prevent insider threats. Taking the right steps can keep your organization safe. Here are the key reasons why implementing insider threat mitigation is crucial for protecting your business.

1. Minimizes Financial and Operational Impact
Insider threats are costly. They can cause financial loss, theft, and disruption. Proactive management of insider risks minimizes costly breaches. It reduces their impact by containing threats early, saving the organization time and resources. This approach boosts productivity. It avoids interruptions from security breaches.
2. Increases Employee Awareness and Accountability
An anticipatory approach often includes security training and awareness programs, which educate employees about security protocols and the importance of data protection. Skilled, responsible employees know the company’s policies on information protection. This reduces the risk of leaks from internal or external sources.
3. Enhances Visibility into Insider Behavior
Behavior analytics and monitoring, give the security team insight into employees’ actions and patterns. These analyses help organizations spot routine processes and insider threats. They improve understanding of security needs and plans. By identifying risks early, organizations can maintain productivity without disruptions caused by insider threats.
How Does Time Champ Secure Your Data from Insider Threats?
Time Champ provides advanced insider threat intelligence focusing on vulnerabilities and comprises significant tools, real-time monitoring, and proactive security measures to ensure comprehensive protection of your data. Here’s how Time Champ works to protect private information from insider threats, ensuring data integrity, privacy, and compliance with regulations.
1. Behavioral Monitoring and Anomaly Detection
Time Champ provides comprehensive monitoring to identify unusual or potentially harmful activities by analyzing user behavior. It tracks keystrokes and mouse movements to detect deviations from typical work patterns. Moreover, Time Champ captures screenshots and records screen activity. So, a user’s desktop can be monitored in great detail. With Time Champ flagging anomalies and sending suspicious activity alerts, security teams can then take swift action against potential internal threats and ensure a secure work environment.
2. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Time Champ implements the role-based access control. Access to data depends on the role and responsibilities an employee needs to perform their job. By ensuring that employees can only access information relevant to their jobs, the risk of sensitive data exposure is minimized. Incorrect access would lead to possible data leaks or compliance issues in organizations with massive sensitive information.
3. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Capabilities
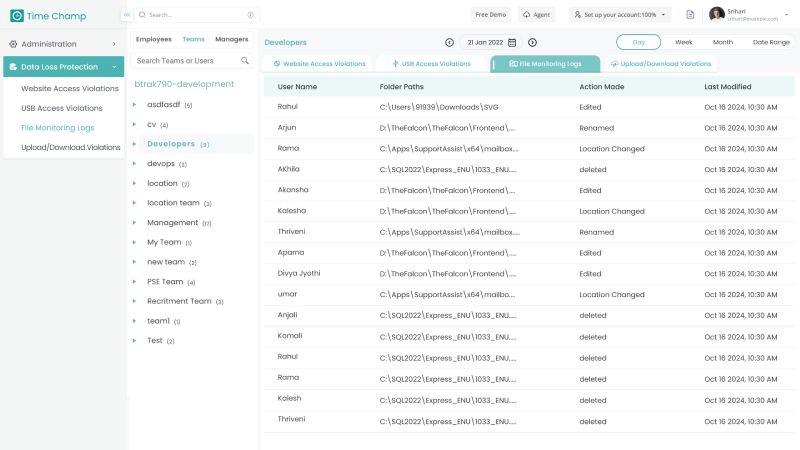
DLP features of Time Champ monitor, detect, and block sensitive data transfer. It helps in setting policies such that unauthorized copying or downloading of information, as well as sending it out to other destinations, can be prevented. Therefore, secure information within the organization is guaranteed. This capacity helps in securing intellectual properties, personal information, and other critical data assets.
Protect your organization from insider threats
Discover how Time Champ strengthens your security today!
Signup for FreeBook DemoConclusion
With all said above, mitigation of the insider threat is key in ensuring protection for your organization. Secured proactive efforts alongside an emphasis on security are ways to minimize risks and boost trust. Keeping yourself aware and focused on safeguarding your data means that your business environment becomes safer as well. This goes to ensuring that your organization remains stable and successful in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
Managing insider threats involves using strict access controls, monitoring insider activity, as well as controlling security in general, and using regular employee training. Some guidelines that should be implemented include; data access and behavioral policies. Ongoing auditing and quick responses to suspicious activities hinder events from occurring in the first place.
Ignoring insider risks exposes an organization to loss of data and funds, legal cases, and reputation loss. It is possible to acquire and harm customer data, which leads to a loss of trust from clients. This in the long run leads to regulatory fines and long-term damaging effects on the credibility of the organization.
It is especially difficult to recognize insiders because they act as colleagues and teammates while performing malicious actions. There exists usually very little resource allocation towards monitoring and very often there is the absence of policy on how to deal with suspicious activity. Moreover, it may also be difficult to introduce effective controls because workers resist security measures that could be in place.
Insider threats include negligent insiders, who make unintentional mistakes, malicious insiders, who intentionally cause harm, and credential thieves, who steal login information to access systems. The threats described above should be noted and understood so that suitable security precautions can be taken.







